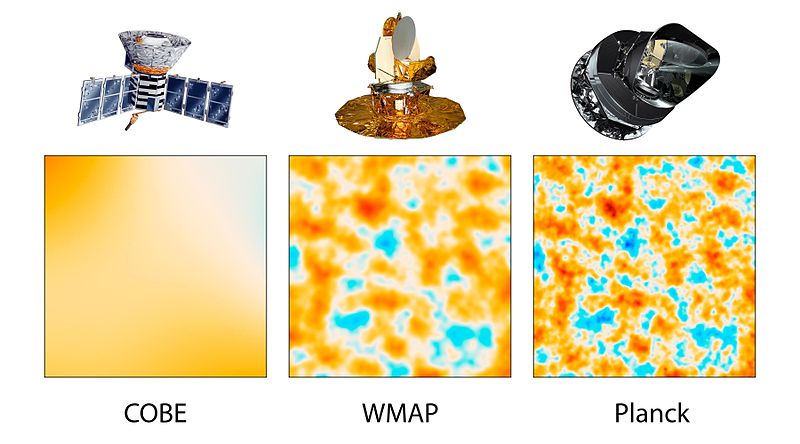
Slika:PIA16874-CobeWmapPlanckComparison-20130321.jpg
Velikost tega predogleda: 800 × 444 točk. Druge ločljivosti: 320 × 178 točk | 640 × 356 točk | 1.024 × 569 točk | 1.280 × 711 točk | 3.600 × 2.000 točk.
Izvorna datoteka (3.600 × 2.000 točk, velikost datoteke: 429 KB, MIME-vrsta: image/jpeg)
Zgodovina datoteke
Kliknite datum in čas za ogled datoteke, ki je bila takrat naložena.
| Datum in čas | Sličica | Velikost | Uporabnik | Komentar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trenutno | 02:48, 23. marec 2013 |  | 3.600 × 2.000 (429 KB) | Nagualdesign | White background. I tried to upload this as a derivative file but Derivative FX kept hanging. (IE9 user.) |
| 04:31, 22. marec 2013 |  | 3.600 × 2.000 (421 KB) | Drbogdan | User created page with UploadWizard |
Uporaba datoteke
Datoteka je del naslednje 1 strani slovenske Wikipedije (strani drugih projektov niso navedene):
Globalna uporaba datoteke
To datoteko uporabljajo tudi naslednji vikiji:
- Uporaba na ar.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na de.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na el.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na en.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na es.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na eu.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na fi.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na fr.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na he.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na id.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na ig.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na it.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na ko.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na nl.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na pl.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na pt.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na ru.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na ru.wikinews.org
- Uporaba na sr.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na sv.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na uk.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na vi.wikipedia.org
- Uporaba na zh.wikipedia.org



